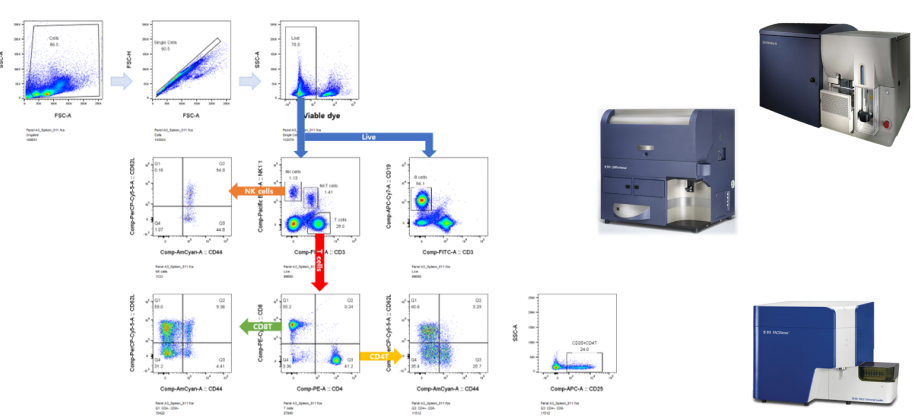
Flow cytometry is a technology commonly used in research on immune responses to analyze changes or functions of immune cells in diseases such as cancer and infection by dyeing cells with fluorescent conjugated antibodies or various fluorescent substances.
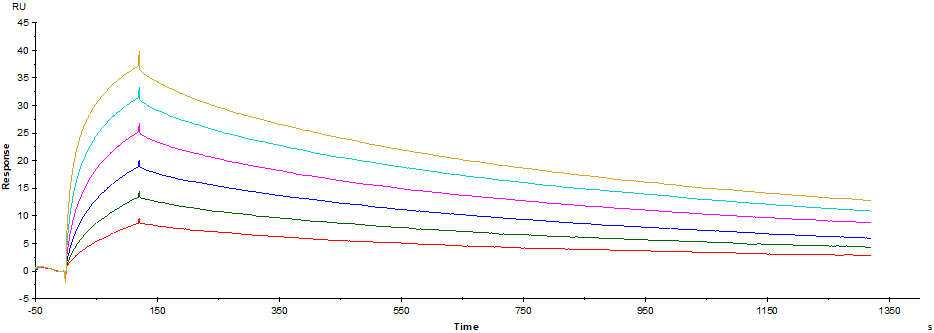
Surface Plasmon Resistance (SPR) analyzes the binding of antigen-antibodies essential for the development of therapeutic antibodies as a method of measuring interactions between biomaterials without sample damage and without labelling such as fluorescent Dye.
pH scouting
CM5 chip
Amine coupling
HBS-EP+buffer
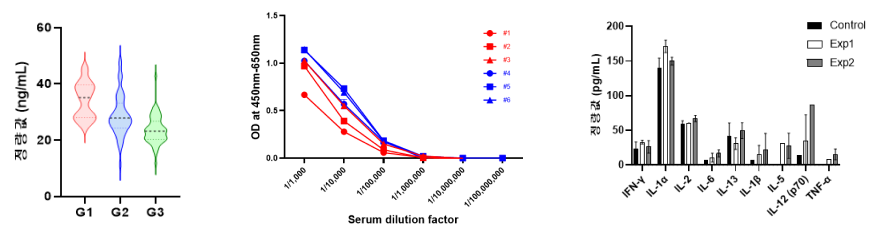
Protein quantitative analysis analyzes biomarkers (cytokines, growth factors) in various biological samples, including cell culture fluid, serum, and plasma, and analyzes them using ELISA and multiplex bead assay.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a method of detecting a sample containing a protein to be analyzed after fixing an antigen or antibody on the surface of a 96-well plate and using an enzyme-bound antibody, and is used for non-clinical and clinical test sample analysis through quantitative analysis using standard substances.
Multiple bead assay is similar to ELISA, but it is a fast and efficient method that analyzes the fluorescent bead with 2 laser with a small amount of sample simultaneously by analyzing the fluorescent bead with a multiplex protein quantitative analysis using fluorescence.